Radar Applications
Technology advances in hardware and software has seen radar employed in an ever increasing range of commercial and military applications. While radar still remains a key technology for the monitoring of aircraft and ships, miniaturization and cost reduction has seen the technology move into many new applications areas including those in the automotive industry, security, non-destructive inspection, meteorology, archeology, mining and surveying.
Spectrum digitizers and arbitrary waveform generators are ideal tools for capturing and creating radar signals. As such, they can play an important role in the development, testing and operation of radar systems and their key components. Spectrum digitizers and arbitrary waveform generators offer a wide range of bandwidths, sampling rates, and dynamic range to match the expanding range of radar measurement needs. When large dynamic range and maximum sensitivity is required high-resolution 14 and 16 bit digitizers are available for capturing and analyzing signals that go up to 250 MHz in frequency. For even higher frequency requirements 8 bit digitizers are available that offer up to 5 GS/s sampling rates and 1.5 GHz bandwidth. The digitizer products can also be used with down-converters to further extend the operational frequency range. Each digitizer card can have from one to four channels (eight channels on lower speed cards) and up to eight cards can be linked together with Spectrum's Star-Hub system to create instruments with up to 32 fully synchronous channels. With large on-board memory (up to 4 GSamples/card) and advanced streaming and readout modes the digitizers are ideal for capturing long and complex radar bursts. Advanced high speed triggering, complete with trigger time stamping, helps to ensure important events are never missed and basic radar parameters such as pulse repetition interval and frequency (PRI and PRF) can be measured with ease. Spectrum's SBench 6 software can also be used to view and qualify I and Q signals as well as helping to characterize timing issues such as leading and trailing edge pulse jitter.
Typical radar applications are diverse and include air and sea traffic control, moving target indication (MTI), Secondary Surveillance radar (SSR), Doppler radar, Synthetic Aperture radar (SAR), Phased array radar, Ground Penetrating radar (GPR), Electronic Warfare, Missile and remotely piloted vehicle guidance systems, Weather radar, Tracking radar, Speed Guns, Over-the-horizon radar (OTH), 3D radar, Automotive radar and Distance measuring equipment (DME).
Spectrum Product Features
- 12, 14 and 16 Bit Resolution
- Sampling rates up to 10 GS/s and Bandwidth over 1.5 GHz
- Segmented Memory with FIFO Readout
- Streaming data to RAID disc array at up to 3 GByte/s continuously
- Low Dead Time between triggers (< 80 ns)
- Acquisition and Generation (Continuous Radar Simulation)
Matching Card Families
Related Documents
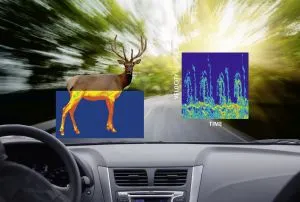
Case Study: Digitizers used for intelligent road-radar to detect wild animals
Every two minutes there is an accident caused by wildlife on German roads at a cost to the insurance industry of more than 600 million euros in 2015 alone. To address this, the Universities of Applied Sciences of Ulm and Heilbronn along with industrial partners have created "SALUS". With a mix of radar, optical cameras and infrared sensors plus neural networks, a machine-learning-system is designed to be able to differentiate between pedestrians, cars, bicyclists, motorbikes, deer, foxes, wild boar etc. predicting the behavior of these objects. The system then sends warnings to car drivers and other road users to prevent accidents. The data of the micro-Doppler radar is gathered by a Spectrum Instrumentation PCIe digitizer card M2p.5926-x4 that provides the required number of channels and bitwidth.

Radar Signal Acquisition and Analysis Using High Speed Modular Digitizers
Radar signals which use pulsed waveform with short duty cycles, multiple modulation types, and critical timing require measurement systems that provide high bandwidth, proportional sample rate, long memory, and fast data transfer. High speed modular digitizers are ideally suited for acquiring and processing radar signals and offer multiple benefits fitted to these measurements. They offer high bandwidth, long acquisition memories, and special acquisition modes to maximize memory usage, these compact instruments provide high speed measurements and analysis of great accuracy. This article will highlight some of the advantages of using high speed modular digitizers for radar system measurements.

Application examples for the ultrafast digitizers of the M5i.33xx series
The five models of the M5i.33xx-x16 digitizer series, with 10 GS/s maximum sampling rate, over 3 GHz bandwidth and 12 bit resolution, are well matched to a broad range of RF and high-speed digital applications. This application notes describes three different examples: measuring of RADAR pusles, Analyzing quadrature-modulated communication-signals and Analysing DDR 2 memory data signals

Case Study: Early warning system for dangerous volcanos with ADC card by Spectrum
A team from University College London (UCL), led by Dr Amin Amiri, is studying the PDCs and developing a radar-based early warning system with a very high level of sensitivity. The core part is a PCIe digitizer card by Spectrum Instrumentation, the model M2p.5921-x4. It is so sensitive that it can detect tiny movements at a distance of six kilometers, which is the distance that the equipment is set up from the slope of the volcano.
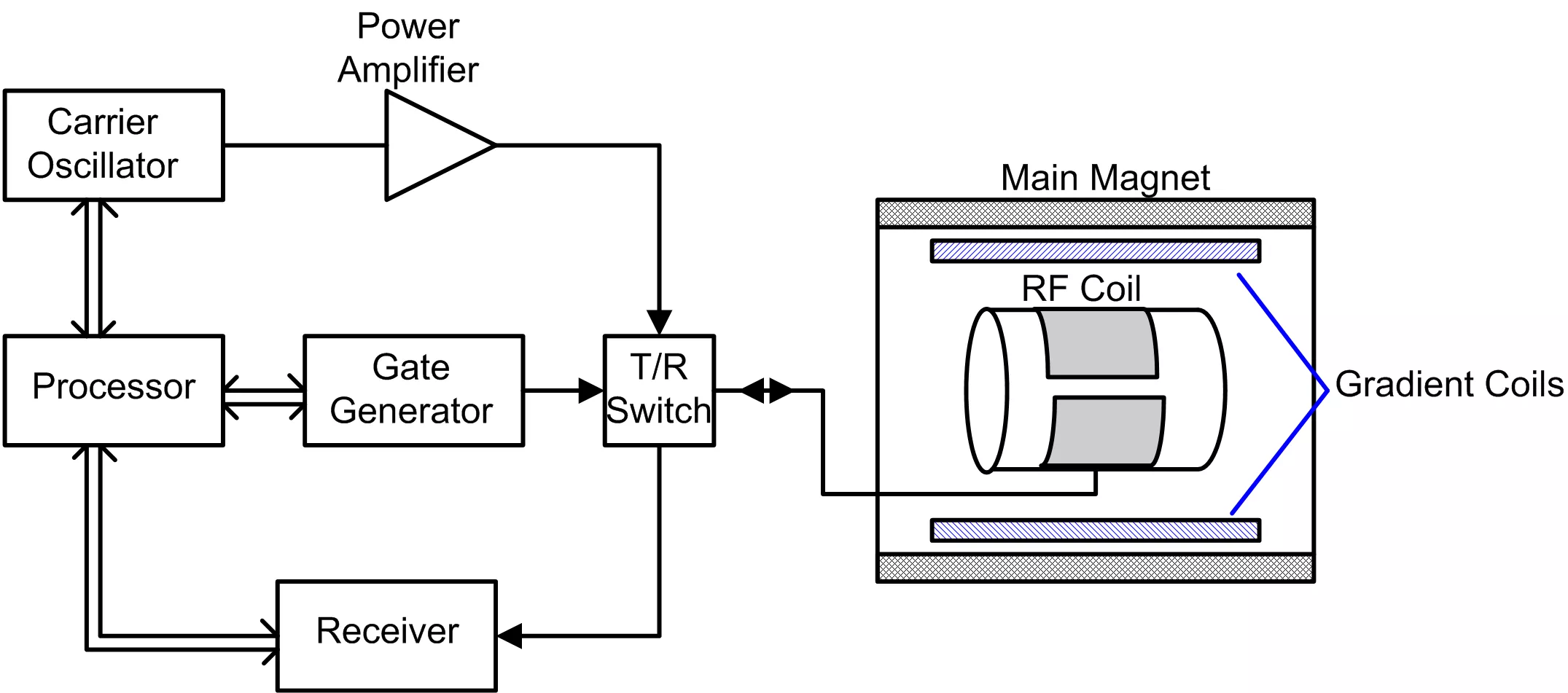
M5i.33xx - Pulse Burst RF Measurements for NMR, MRI and radar
Many RF systems operate using burst modes where radio frequency (RF) signals are transmitted for a short period. Examples of this kind of operation include echo-ranging applications like radar, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and relaxation radiation detection in nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR). These applications transmit a burst of relatively high-power RF and then wait for a return echo or a relaxation radiation signal. Measurement of this type of signal requires instruments with wide bandwidth, high sampling rate, long acquisition memory, fast processing, and high-speed data streaming.
Research Papers
Space Debris Tracking
At the Polytechnic University of Madrid’s, Technical School of Telecommunications Engineering, in Spain, they are studying how radar systems can be improved to allow better tracking of space debris orbiting earth. A masters paper discussing how signal generation can be adapted and optimized is below (in Spanish) with data acquired using an M4i.4420-x8, 250 MS/s, 16 bit, digitizer
Masters Paper (Spanish)Software Defined Radio with GPU Accelerator
The Department of Security and Crime Science, at the University College London, UK has been studying ways to create a high- speed Software Defined Radar (SDRadar) system. Using a GPU accelerator with a 16-channel DN2.593-16 80 MS/s, 16 bit LXI Digitizer they have developed a system that overcomes processing speed limitations when using a CPU only. A paper discussing their work and results can be found here:
Research PaperUsing Radar for Human Identification
At the Key Laboratory of Radar Imaging and Microwave Photonics, Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics , in China they are using an M2i.4912 10 MS/s, 16-bit Digitizer for signal acquisition in a radar system that uses micro-Doppler signatures and deep convolutional neural networks for human identification. A reference paper on the subject can be found here:
Research Paper