THIS PRODUCT IS END-OF-LIFE. Show more about end-life-products policy.
Product:
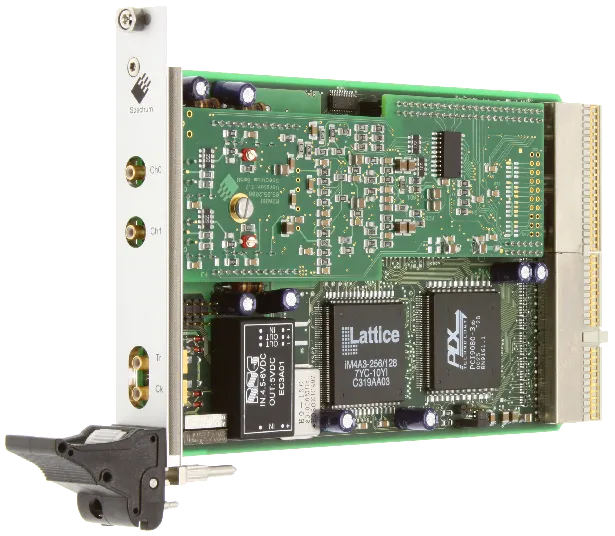
MX.4710
16 bit transient recorder
Description:
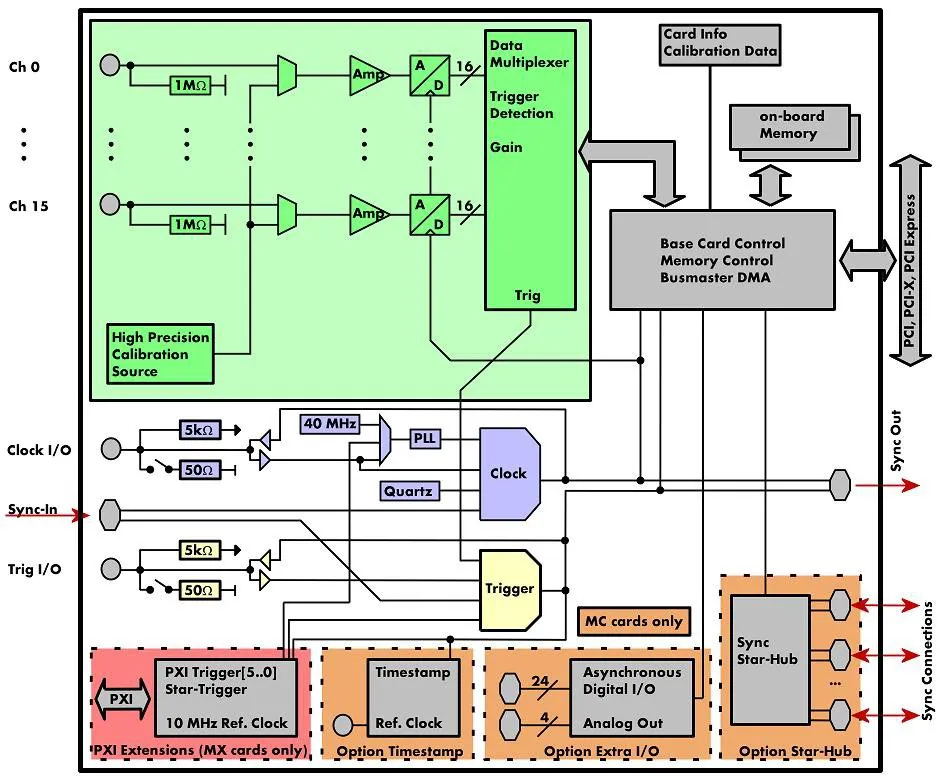
The MX.47xx for the first time offers full 16 bit resolution synchronously on eight channels at high sampling rates. Every channel has its own amplifier and A/D converter. This eliminates the problems known from multiplexed systems like phase error between the channels or high crosstalk. Every input channel can be offset and gain calibrated by software using a high precision onboard calibration source. Three different models are available, each in a different speed grade. These versions are working with sampling rates of 100 kS/s, 250 kS/s or 500 kS/s. The boards can also be updated to a multi-channel system using the PXI backplane signals.
Facts & Features:
- Up to 100 kS/s on 8 channels
- Simultaneously sampling on all channels
- Separate ADC and amplifier per channel
- Complete on-board calibration
- 8 input ranges: +/-50 mV up to +/-10 V
- Up to 64 MSample on-board memory
- 32 MSample standard memory installed
- Window, pulse width, re-arm trigger
- Synchronization possible
- CompactPCI/PXI 3U compatible
- Supporting PXI star trigger
- Supporting PXI trigger bus
- Supporting PXI reference clock
Application examples:
- Production tests
- Massive multi-channel systems
- High-speed temperature and strain gauge measurements
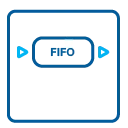
FIFO mode
The FIFO mode is designed for continuous data transfer between measurement board and PC memory (with up to 100 MByte/s) or hard disk. The control of the data stream is done automatically by the driver on interrupt request. The complete installed on-board memory is used for buffer data, making the continuous streaming extremely reliable.PXI Star Trigger Card (Optional)
The MX.9010 is a special PXI star trigger card designed for the Spectrum PXI products. It allows to route clock and trigger synchronously to all PXI slots that are connected to the star trigger slot. The PXI reference clock is overwritten and external trigger events are synchronized to the sampling clock.

Channel Trigger
The data acquisition boards offer a wide variety of trigger modes. Besides the standard signal checking for level and edge as known from oscilloscopes it's also possible to define a window trigger. Trigger conditions can be combined with logical conjunctions like OR to adopt to different application scenarios.
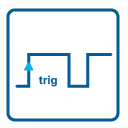
External Trigger
All boards can be triggered using an external TTL signal. It's possible to use positive or negative edge also in combination with a programmable pulse width. An internally recognized trigger event can - when activated by software - be routed to the trigger connector to start external instruments.


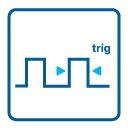
PXI Trigger
The Spectrum cards support star trigger as well as the PXI trigger bus. using a simple software commend one or more trigger lines can be used as trigger source. This feature allows the easy setup of OR connected triggers from different cards.
Timestamp
The timestamp option writes the time positions of the trigger events in an extra memory. The timestamps are relative to the start of recording, a defined zero time, externally synchronized to a radio clock, or a GPS receiver. With this option acquisitions of systems on different locations can be set in a precise time relation.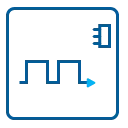
External Clock
Using a dedicated connector a sampling clock can be fed in from an external system. It's also possible to output the internally used sampling clock to synchronize external equipment to this clock.

PXI Reference Clock
The card is able to use the 10 MHz reference clock that is supplied by the PXI system. Enabled by software the PXI reference clock is feeded in the on-board PLL. This feature allows the cards to run with a fixed phase relation.
Reference Clock
The option to use a precise external reference clock (normally 10 MHz) is necessary to synchronize the board for high-quality measurements with external equipment (like a signal source). It's also possible to enhance the quality of the sampling clock in this way. The driver automatically generates the requested sampling clock from the fed in reference clock.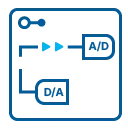
On-board Calibration
The on-board calibration can be run on user request and calibrates the amplifier against a dedicated internal high precision calibration source. After this calibration data is stored permanently in an on-board EEPROM and is automatically used for further acquisitions.
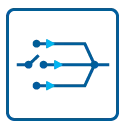
Programmable Input Amplifiers
The analog inputs can be adapted to real world signals using individual settings for each channel. A large number of different input ranges allow to adopt perfectly to the real world signals.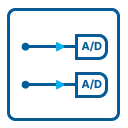



This standard driver is included in the card delivery and it is possible to get the newest driver version free of charge from our homepage at any time. There are no additional SDK fees for the classical text-based programming. All boards are delivered with drivers for Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10 and Windows 11, all 32 bit and 64 bit.
| Product | Channels | Max. Samplerate | Max. Bandwidth |
|---|---|---|---|
| MX.4720 | 8 | 250 KS/s | 125 KHz |
| MX.4730 | 8 | 500 KS/s | 250 KHz |
| On different platforms | Bus | Max. Bus Transfer speed |
|---|---|---|
| M2i.4710 | PCI-X | 245 MByte/s |
| M2i.4710-Exp | PCI Express x1 | 160 MByte/s |
| MC.4710 | CompactPCI | 100 MByte/s |
Documents
Data sheet of the MX.47xx family |
21.02.2022 | 309 K | ||
Manual of MX.47xx family |
21.02.2022 | 3 M | ||
Data sheet of SBench 6 |
15.01.2024 | 999 K | ||
Manual for MATLAB drivers for MI/MC/MX |
21.02.2022 | 70 K | ||
LabVIEW Manual for MC/MX.47xx |
21.02.2022 | 758 K | ||
Manual for SBench 6 |
21.02.2022 | 7 M |
WINDOWS DRIVER + SOFTWARE
MI/MC/MX/PCI.xxx Windows 98/NT 32 Bit Drivers |
21.02.2022 | 353 K | ||
MI/MC/MX/PCI.xxx Windows XP/Vista 32 Bit Drivers |
21.02.2022 | 381 K | ||
MI/MC/MX/PCI.xxx Windows XP/Vista 64 Bit Drivers |
21.02.2022 | 579 K | ||
MI/MC/MX/PCI.xxx Windows 7/8 32 Bit Drivers |
4 | 21.02.2022 | 397 K | |
MI/MC/MX/PCI.xxx Windows 7/8 64 Bit Drivers |
4 | 21.02.2022 | 604 K | |
MI/MC/MX/PCI.xxx Windows 10 32 Bit Drivers |
4 | 21.02.2022 | 415 K | |
MI/MC/MX/PCI.xxx Windows 10/11 64 Bit Drivers |
4 | 21.02.2022 | 627 K | |
C/C++ driver header and library files |
7.00 | 23.02.2024 | 43 K | |
SBench 5 Installer |
5.3.0 | 21.02.2022 | 5 M | |
SBench 6 (32-bit) Installer / Windows 7, 8, 10 |
6.5.07 | 23.02.2024 | 36 M | |
SBench 6 (64-bit) Installer / Windows 7, 8, 10, 11 |
6.5.07 | 23.02.2024 | 39 M | |
MI / MC / MX MATLAB driver + examples |
21.02.2022 | 714 K | ||
MI / MC / MX LabVIEW Driver |
21.02.2022 | 8 M | ||
MI / MC / MX Examples for C/C++, Delphi, VB, LabWindows/CVI, ... |
21.02.2022 | 700 K |
LINUX DRIVER + SOFTWARE
MI / MC / MX Linux 32 bit and 64 bit Drivers |
4 | 21.02.2022 | 18 M | |
SBench 6 Linux 32 (.rpm) |
6.5.07 | 23.02.2024 | 26 M | |
SBench 6 Linux 64 (.rpm) |
6.5.07 | 23.02.2024 | 26 M | |
SBench 6 Linux 32 (.deb) |
6.5.07 | 23.02.2024 | 23 M | |
SBench 6 Linux 64 (.deb) |
6.5.07 | 23.02.2024 | 22 M | |
SBench6 Jetson (.deb) |
6.5.07 | 23.02.2024 | 8 M | |
MI / MC / MX Linux Examples (C/C++) |
21.02.2022 | 53 K |
Firmware
Product Notes
| General Digitizer Introduction | General Introduction to Waveform Digitizers |
21.02.2022 | 587 K | |
| High-Res High BW Digitizers | Advantages of High Resolution in High Bandwidth Digitizers |
21.02.2022 | 2 M | |
| Digitizer Acquisition Modes | Using modular Digitizer Acquisition Modes |
21.02.2022 | 3 M | |
| Digitizer Front-End | Proper Use of Digitizer Front-End Signal Conditioning |
21.02.2022 | 3 M | |
| Trigger and Sync | Trigger, Clock and Synchronization Details at high-speed Digitizers |
21.02.2022 | 1 M | |
| SBench 6 Introduction | SBench 6 - Data Acquisition and Analysis of Digitizer Data |
21.02.2022 | 1 M |
Application Notes
| Ultrasonic Applications | Using Digitizers in Ultrasonic Applications |
21.02.2022 | 617 K | |
| Signal Processing Tools | Using Signal Processing Tools to enhance Digitizer Data |
21.02.2022 | 1 M | |
| Mechanical Measurements | Mechanical Measurements Using Digitizers |
21.02.2022 | 1 M | |
| Power Measurements | Power Measurements Using Modular Digitizers |
21.02.2022 | 1 M | |
| Using Probes & Sensors | Using Probes and Sensors with Modular Digitizers |
21.02.2022 | 858 K | |
| Teaming AWG with Digitizer | Teaming an Arbitrary Waveform Generator with a Modular Digitizer |
21.02.2022 | 919 K | |
| Common Digitizer Setup Problems | Application Note: Common Digitizer Setup Problems to avoid |
21.02.2022 | 1 M | |
| AN Amplitude Resolution | Application Note: The Amplitude Resolution of Digitizers and how it affects Measurements |
21.02.2022 | 555 K |